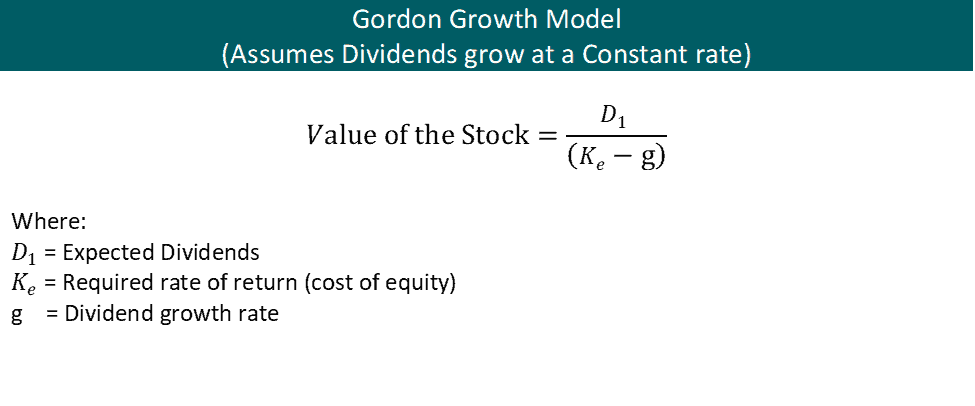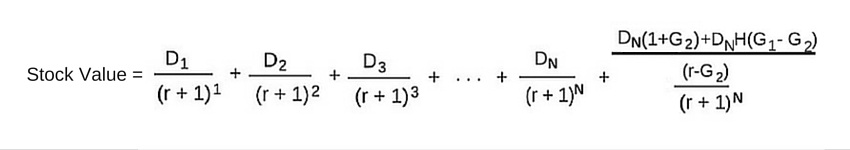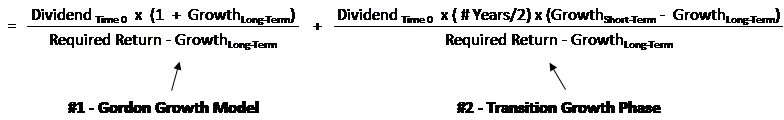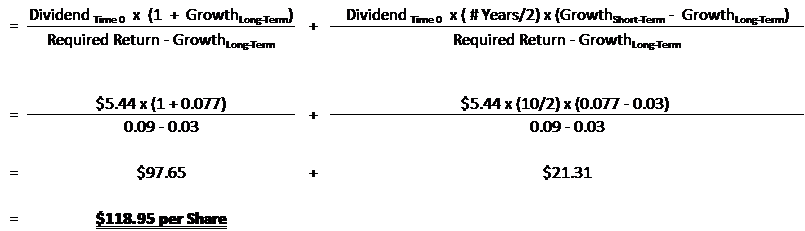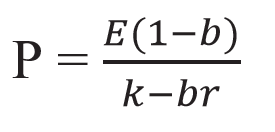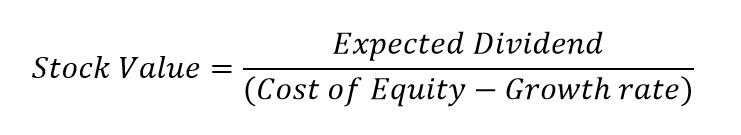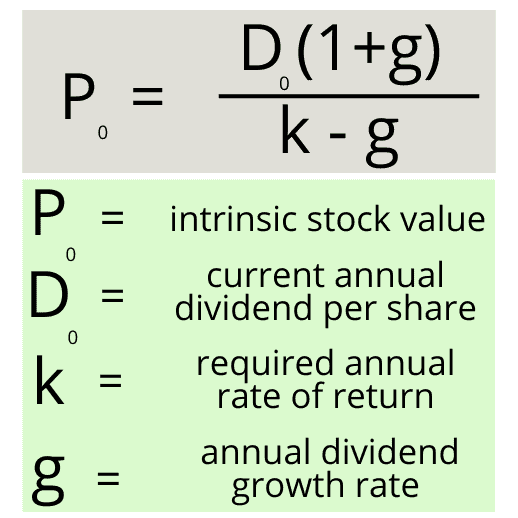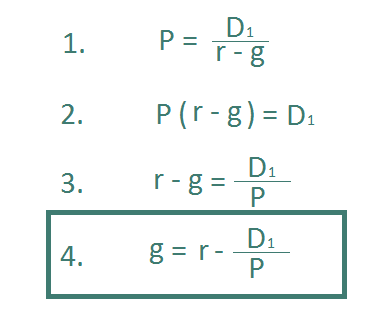Gordon Model Of Dividend
Investors can then compare companies against other industries using this simplified model.

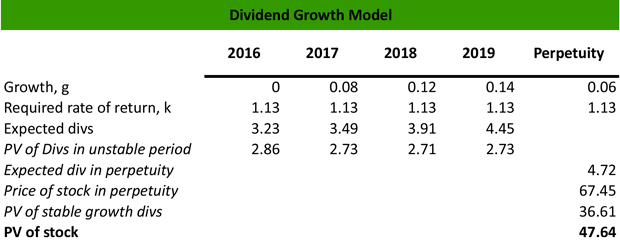
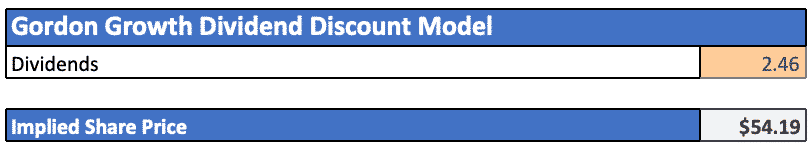
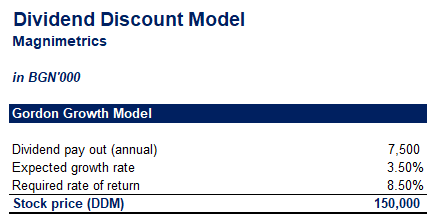
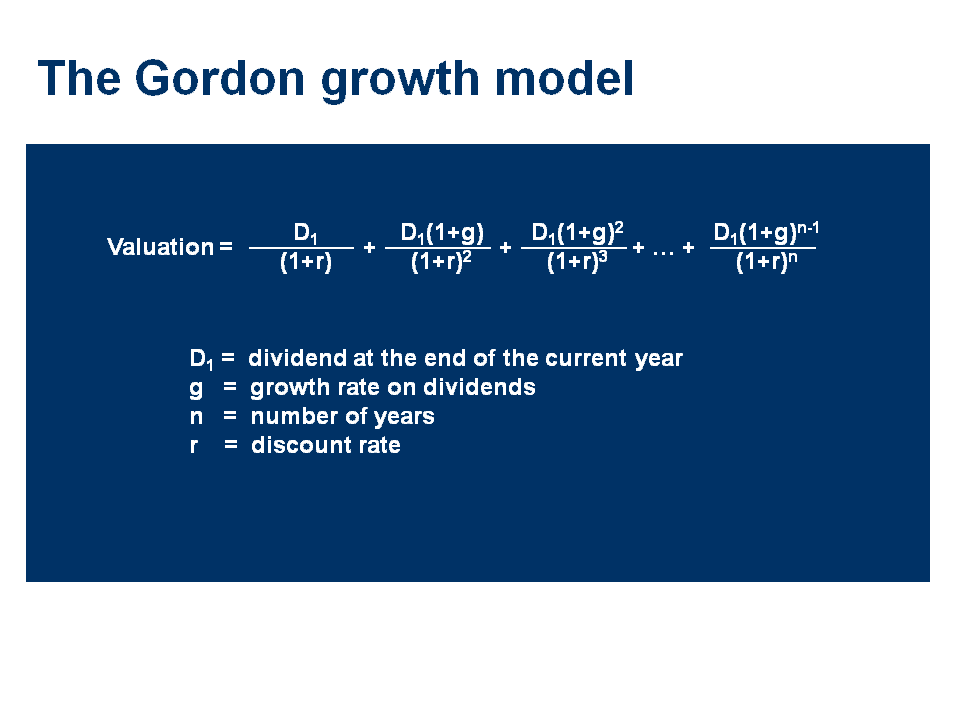
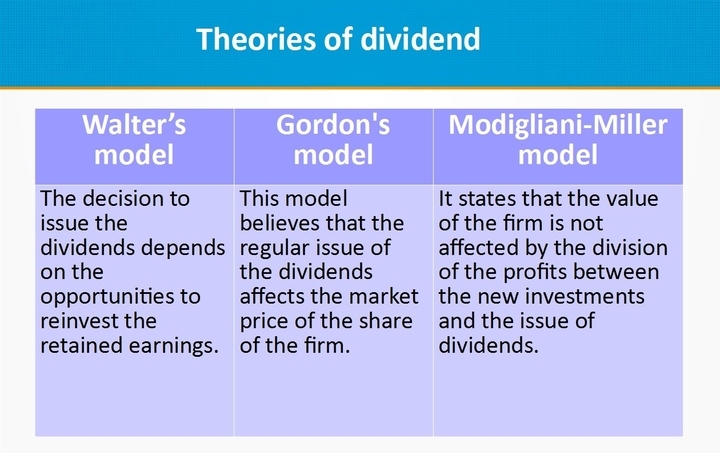
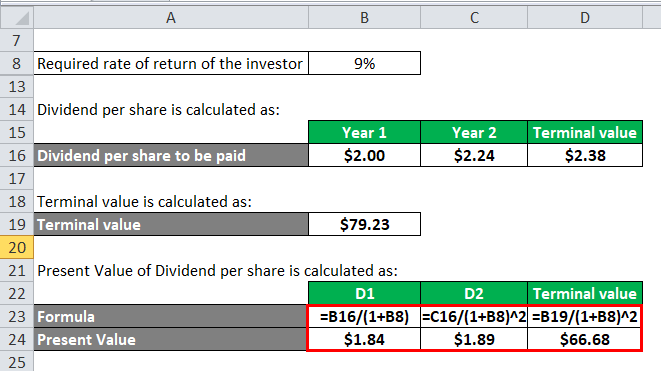
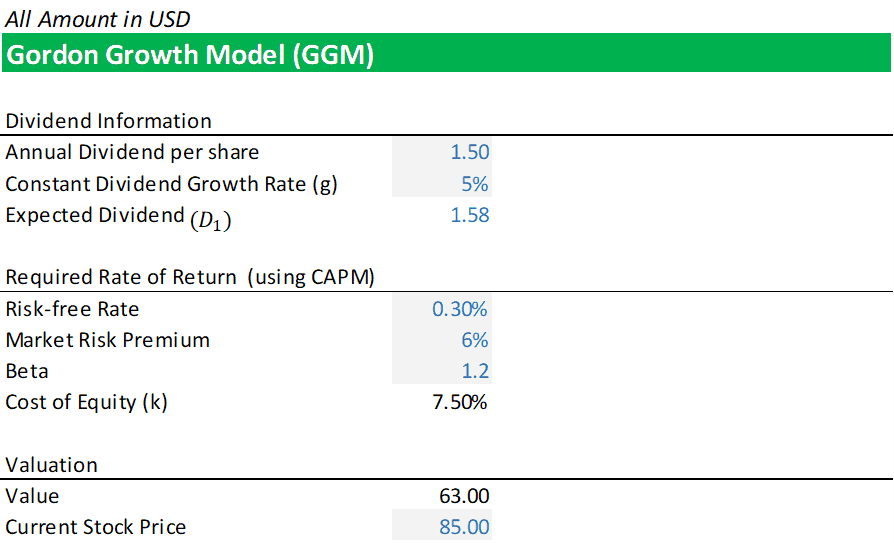
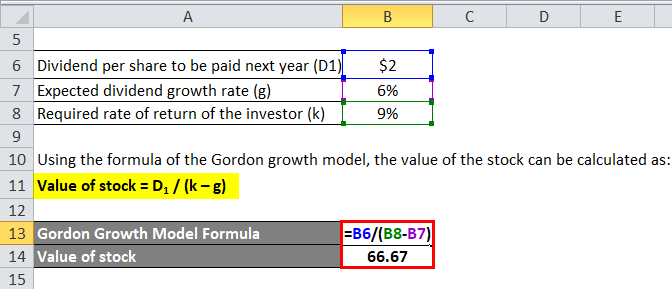
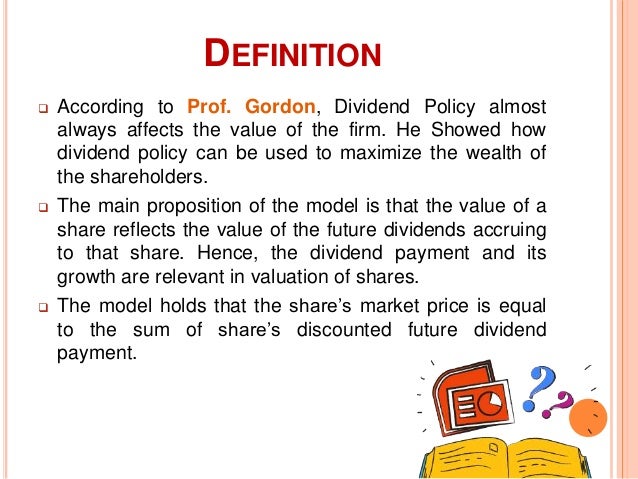
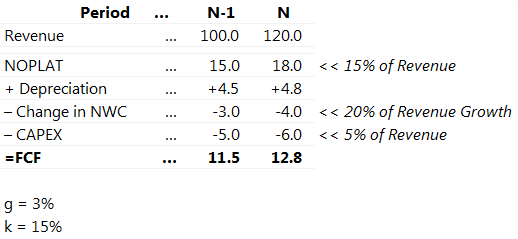
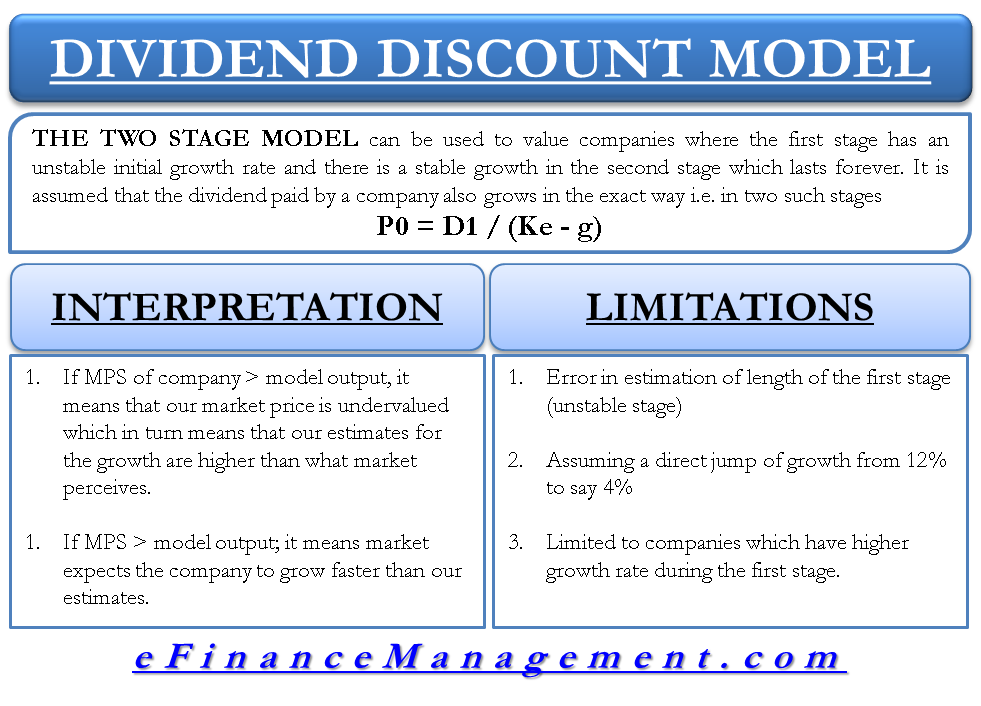
Gordon model of dividend. Gordon growth model is based on the dividend discount model ddm and was developed by professor myron j. Gordon growth model is a type of dividend discount model in which not only the dividends are factored in and discounted but also a growth rate for the dividends is factored in and the stock price is calculated based on that. According to the gordons model the market value of the share is equal to the present value of future dividends.
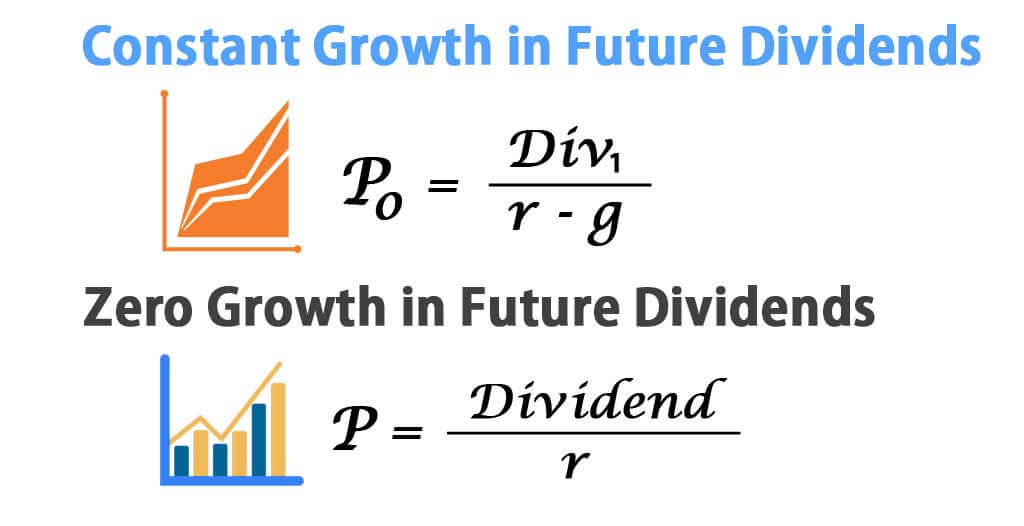
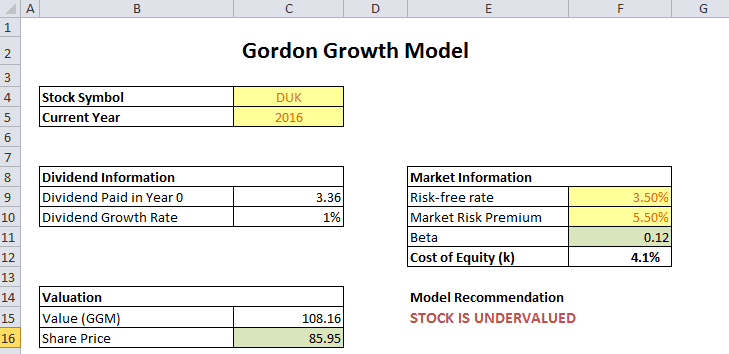
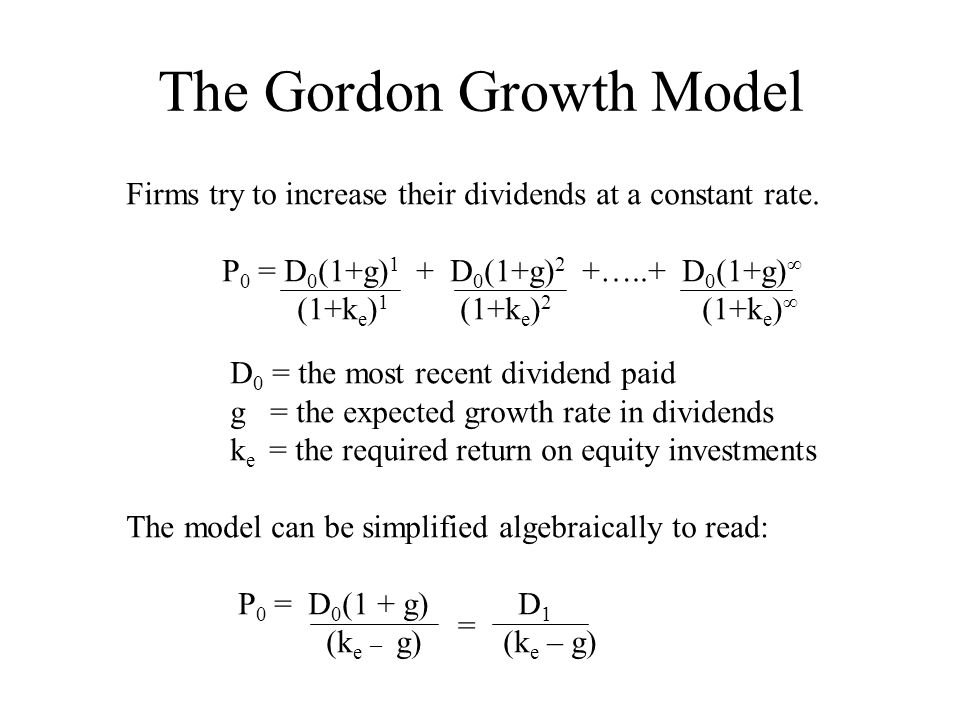
It is represented as. The gordon growth model ggm values a companys stock using an assumption of constant growth in dividends. The gordon growth model also known as the gordon dividend model or dividend discount model is a stock valuation method that calculates a stocks intrinsic value regardless of current market conditions.
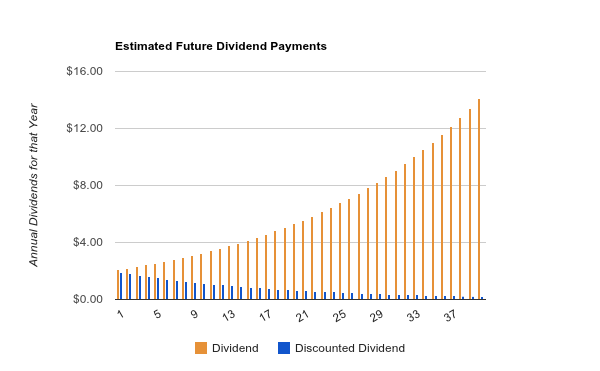
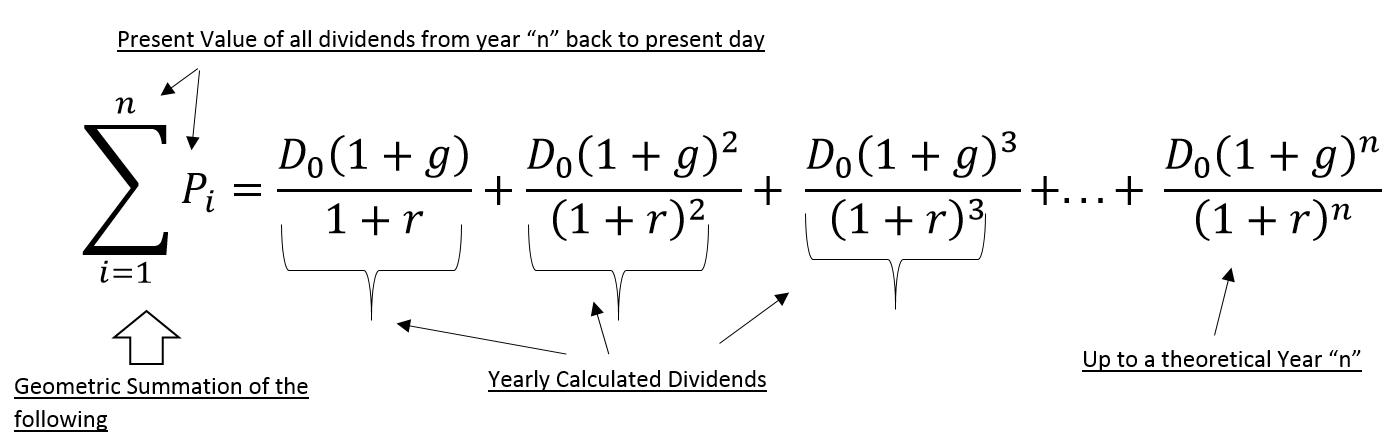
The model takes the infinite series of dividends per share and discounts them back into. Sometimes you will hear this tool referred to as a constant perpetual growth model. Or at times just the constant growth model.
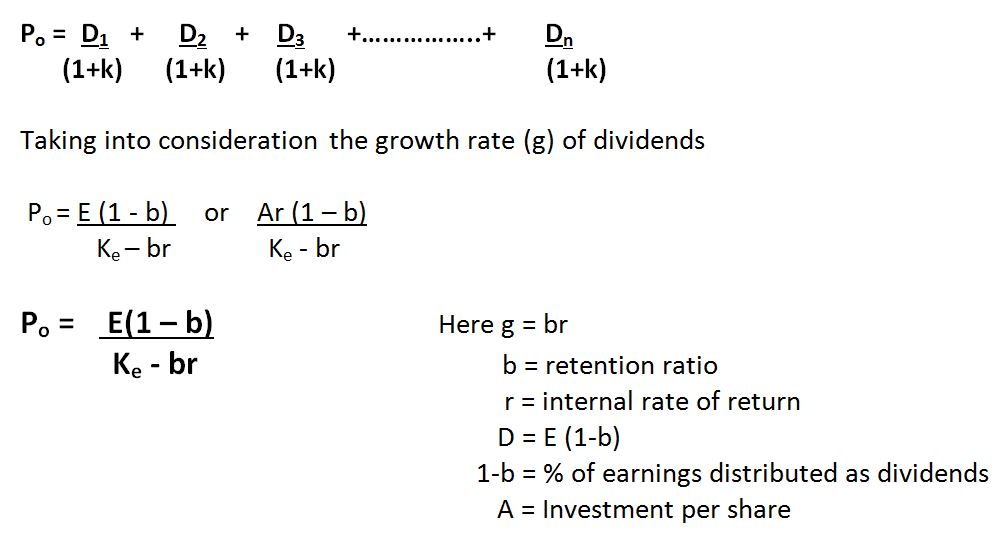
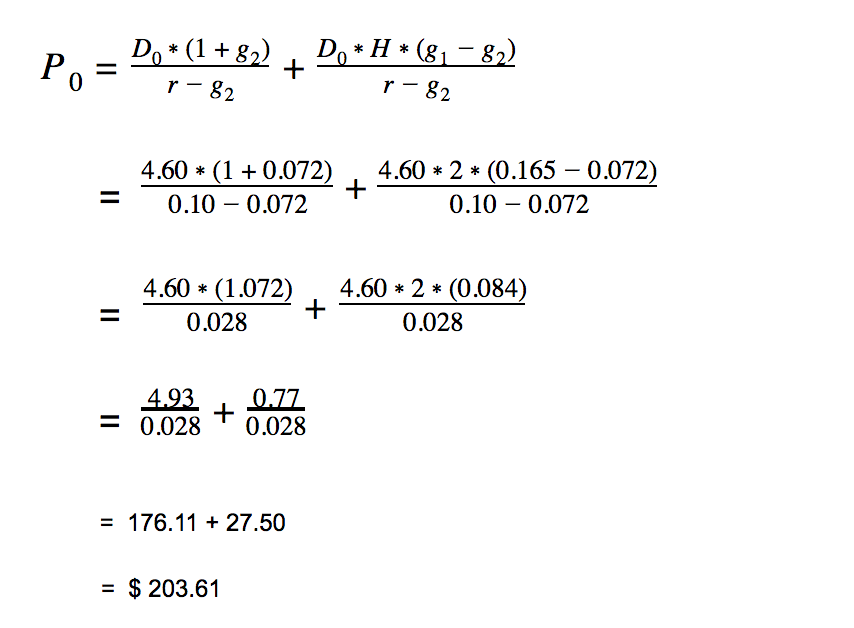
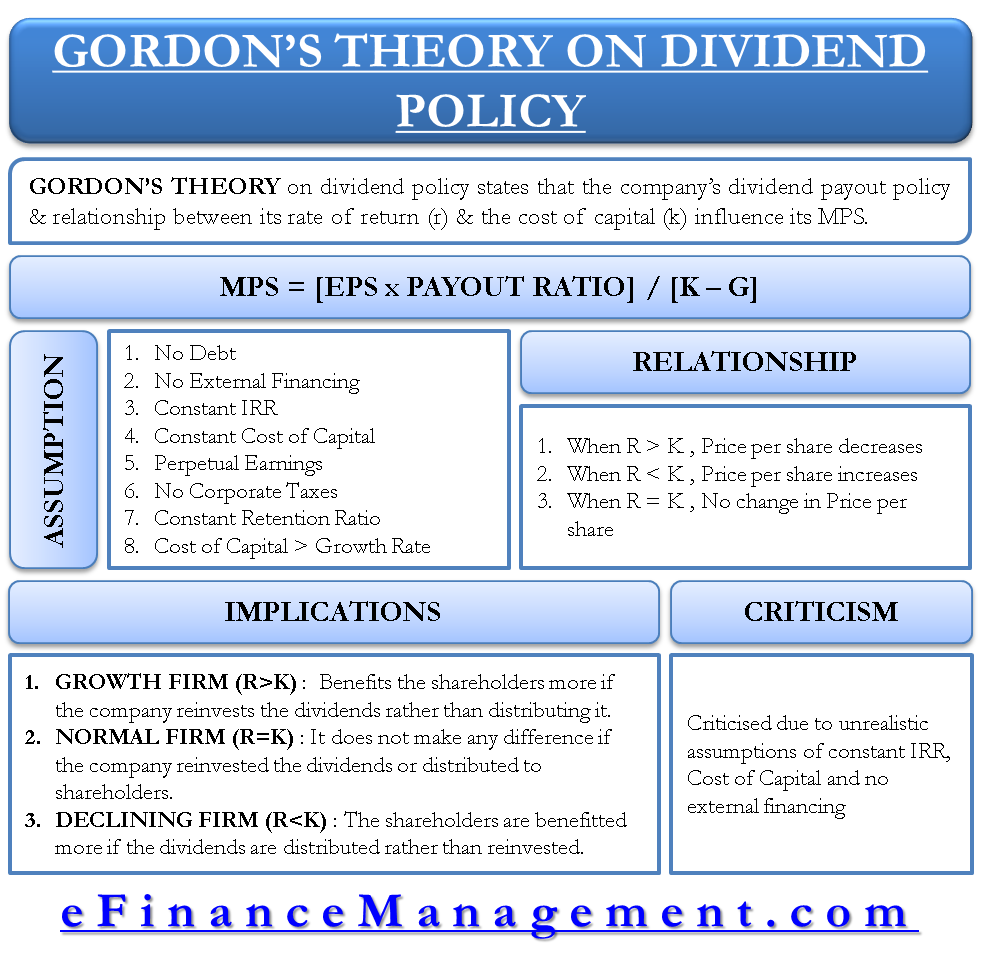
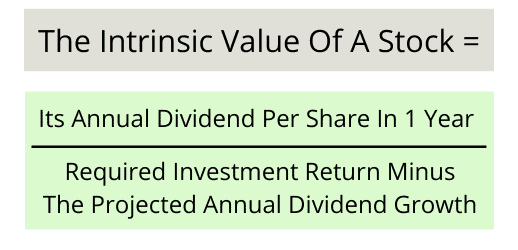
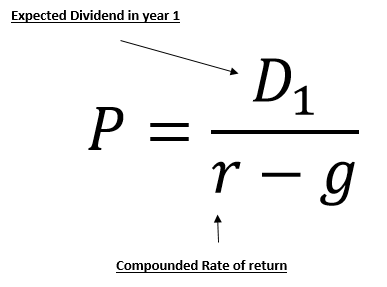
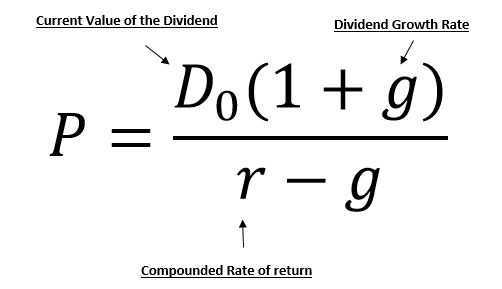
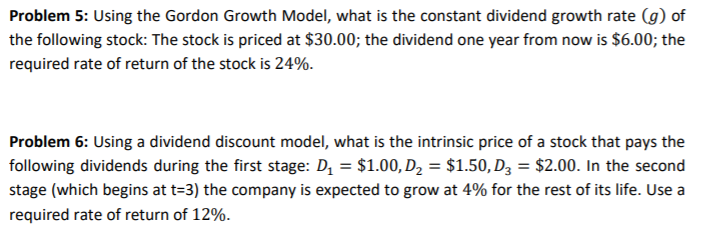
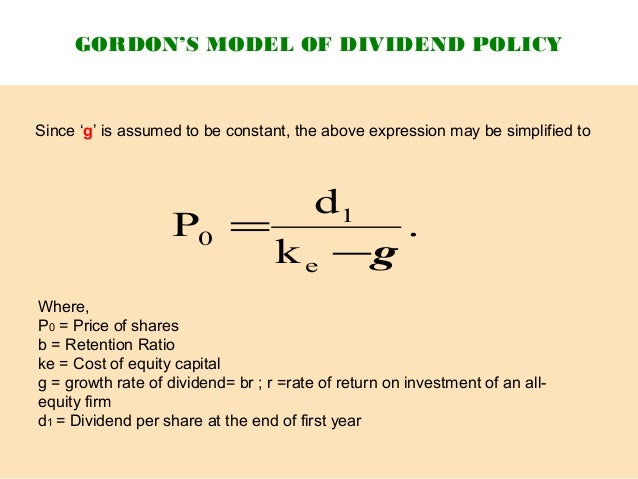
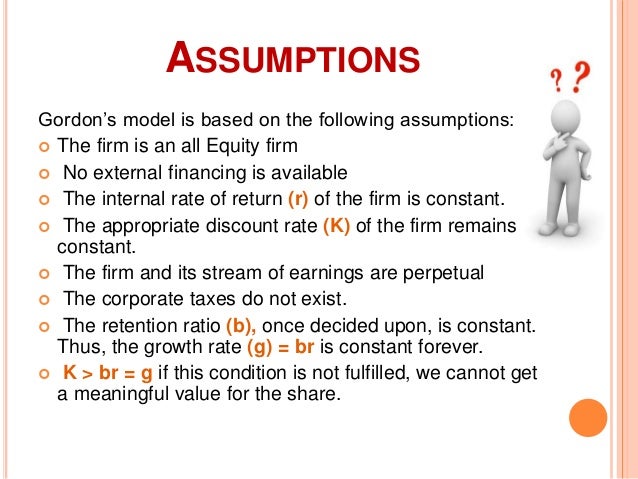
It relates the value of a stock to its expected future dividends the cost of equity and the expected growth rate in dividends. Assumptions of gordons model. D n 1 1 r e n 1 d n 1 r e n p n 1 r e n p 0 d 1 p 0 d 1 r e g r e d 1 p 0 g divid payout ratio t earnings ret ratio t 1 dividend t earnings t shares t x divid payout ratio t g.
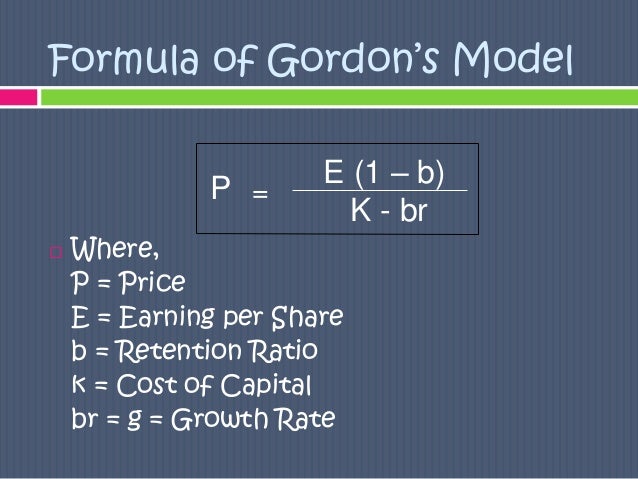
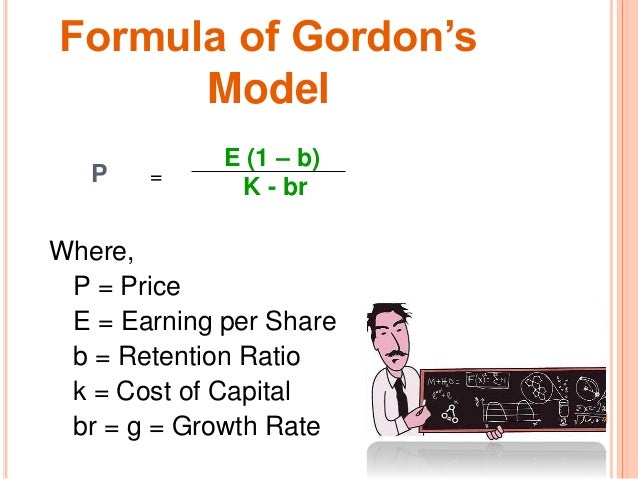
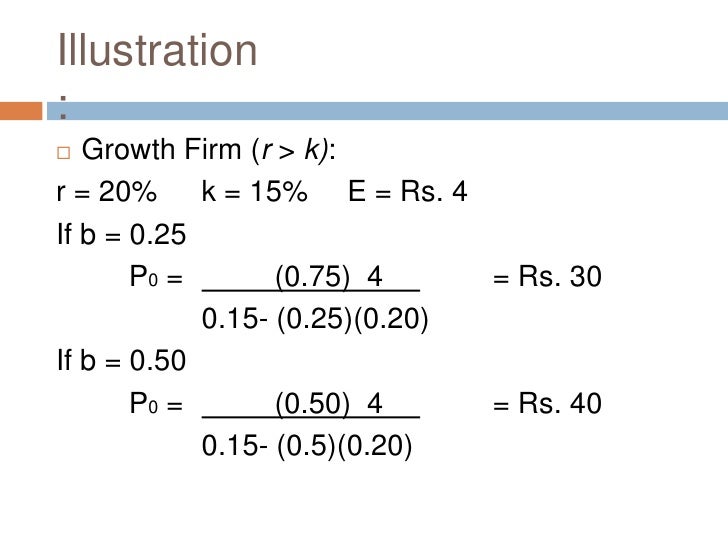
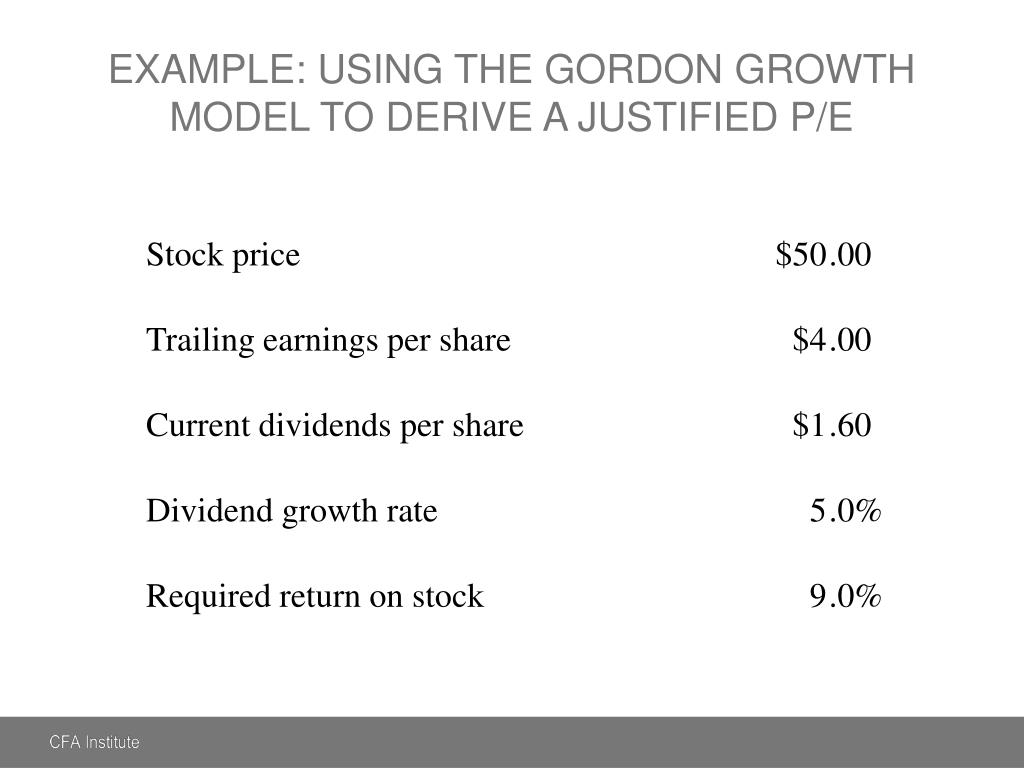
And more specifically the value of a dividend growth stock. Gordon of the university of toronto in the late 1950s. P e 1 b ke br.
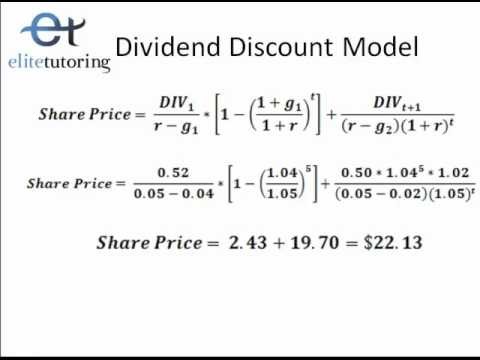
Where p price of a share e earnings per share b retention ratio 1 b proportion of earnings distributed as dividends ke capitalization rate br growth rate. Under the ddm estimating the future dividends of a company could be a complex task since dividend payouts of companies may vary due to other factors such as market conditions profitability and so on.